Dmidecode is a tool or command which is used to retrieve the useful information of your system’s hardware components in human readable format. Dmidecode is available for all the Linux like systems (RHEL, CentOS, Debian and SUSE). Dmidecode stands for DMI (Desktop Management Interface) table decoder, as the name suggests it reads the data from DMI table and represents to us in human readable format. DMI table holds the system hardware details like BIOS, Serial Number, RAM(DIMMs) and CPU details etc, apart from this dmidecode can also retrieve details about the maximum system supported configuration (like DIMMs & Processors etc).
In this article we will try to cover 12 useful dmidecode examples for Linux systems.
Example 1) Understanding dmidecode command output
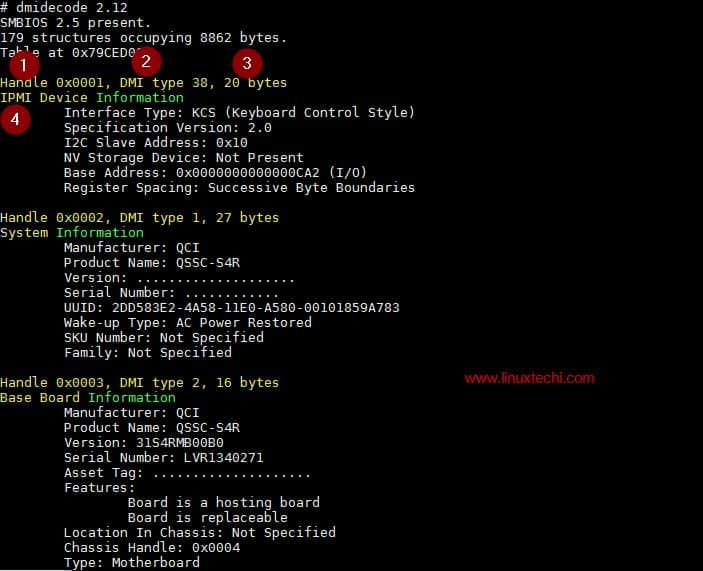
When we run the dmidecode command then it displays the output on the screen, in the output we have the records, each record has 4 different values.
- Handle – Unique identifier number
- Type – It tells about the hardware components, in below example DMI type 38 refers to IPMI device
- Size – Size of record
- Decoded value – Information about the type of record, in the below example decoded values of IPMI device are Interface Type, Specification Version, Base Address & Register Spacing
Let’s run the dmidecode command,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode | more
Output would be something like below
Example 2) Different DMI types used in dmidecode command
Followings are the DMI types that are used on dmidecode command
Type Information -------------------------------------------- 0 BIOS 1 System 2 Baseboard 3 Chassis 4 Processor 5 Memory Controller 6 Memory Module 7 Cache 8 Port Connector 9 System Slots 10 On Board Devices 11 OEM Strings 12 System Configuration Options 13 BIOS Language 14 Group Associations 15 System Event Log 16 Physical Memory Array 17 Memory Device 18 32-bit Memory Error 19 Memory Array Mapped Address 20 Memory Device Mapped Address 21 Built-in Pointing Device 22 Portable Battery 23 System Reset 24 Hardware Security 25 System Power Controls 26 Voltage Probe 27 Cooling Device 28 Temperature Probe 29 Electrical Current Probe 30 Out-of-band Remote Access31 Boot Integrity Services 32 System Boot 33 64-bit Memory Error 34 Management Device 35 Management Device Component 36 Management Device Threshold Data 37 Memory Channel 38 IPMI Device 39 Power Supply 40 Additional Information 41 Onboard Devices Extended Information 42 Management Controller Host Interface
Keyword Types ------------------------------ bios 0, 13 system 1, 12, 15, 23, 32 baseboard 2, 10, 41 chassis 3 processor 4 memory 5, 6, 16, 17 cache 7 connector 8 slot 9
Example 3) Display hardware information using type id
In dmidecode command we can use either keyword or type id to get hardware information of system, In example 2 we have already listed the keyword and its type id. let’s assume we want to display cache information of your system, then we can run any of the below command,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t cache Or [root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t 7 # dmidecode 2.12 SMBIOS 2.5 present. Handle 0x009C, DMI type 7, 19 bytes Cache Information Socket Designation: L1-Cache Configuration: Enabled, Not Socketed, Level 1 Operational Mode: Write Back Location: Internal Installed Size: 192 kB Maximum Size: 192 kB Supported SRAM Types: Synchronous Installed SRAM Type: Synchronous Speed: Unknown Error Correction Type: Single-bit ECC System Type: Data Associativity: 8-way Set-associative Handle 0x009D, DMI type 7, 19 bytes Cache Information Socket Designation: L1-Cache Configuration: Enabled, Not Socketed, Level 1 Operational Mode: Write Back Location: Internal Installed Size: 192 kB Maximum Size: 192 kB Supported SRAM Types: Synchronous Installed SRAM Type: Synchronous Speed: Unknown Error Correction Type: Single-bit ECC System Type: Instruction Associativity: 4-way Set-associative …………………………………………………………………………
Read More : 10 tips about ‘dmesg’ command for Linux Geeks
Example 4) Display the Information about BIOS
Run below dmidecode command followed by bios as type
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode --type bios Or [root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t bios # dmidecode 2.12 SMBIOS 2.5 present. Handle 0x0005, DMI type 0, 24 bytes BIOS Information Vendor: Intel Corp. Version: QSSC-S4R.QCI.01.00.0037.061120141015 Release Date: 06/11/2014 Address: 0xF0000 Runtime Size: 64 kB ROM Size: 16384 kB Characteristics: PCI is supported PNP is supported BIOS is upgradeable BIOS shadowing is allowed Boot from CD is supported Selectable boot is supported EDD is supported 3.5"/2.88 MB floppy services are supported (int 13h) Print screen service is supported (int 5h) 8042 keyboard services are supported (int 9h) Serial services are supported (int 14h) CGA/mono video services are supported (int 10h) ACPI is supported USB legacy is supported LS-120 boot is supported ATAPI Zip drive boot is supported Function key-initiated network boot is supported Targeted content distribution is supported BIOS Revision: 17.18 Firmware Revision: 0.0
Example 5) Display Hardware Information about the Chassis
Run the following dmidecode command to display information about the chassis
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t chassis
# dmidecode 2.12
SMBIOS 2.5 present.
Handle 0x0004, DMI type 3, 22 bytes
Chassis Information
Manufacturer: ..............................
Type: Main Server Chassis
Lock: Not Present
Version: 32S4RCS0010
Serial Number: QTFCVR1110136
Asset Tag: ....................
Boot-up State: Safe
Power Supply State: Safe
Thermal State: Safe
Security Status: Unknown
OEM Information: 0x01000181
Height: 1 U
Number Of Power Cords: 1
Contained Elements: 0
SKU Number: Not Specified
Example 6) Display Hardware Information about baseboard
Execute the beneath dmidecode command to display hardware information about your system baseboard,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t baseboard
# dmidecode 2.12
SMBIOS 2.5 present.
Handle 0x0003, DMI type 2, 16 bytes
Base Board Information
Manufacturer: QCI
Product Name: QSSC-S4R
Version: 31S4RMB00B0
Serial Number: LVR1340271
Asset Tag: ....................
Features:
Board is a hosting board
Board is replaceable
Location In Chassis: Not Specified
Chassis Handle: 0x0004
Type: Motherboard
Contained Object Handles: 0
Handle 0x0027, DMI type 10, 6 bytes
On Board Device Information
Type: Video
Status: Enabled
Description: ServerEngines Pilot II
Handle 0x0028, DMI type 10, 6 bytes
On Board Device Information
Type: Ethernet
Status: Enabled
Description: Intel Dual GbE #1
Handle 0x0029, DMI type 10, 6 bytes
On Board Device Information
Type: Ethernet
Status: Enabled
Description: Intel Dual GbE #2
Handle 0x002A, DMI type 10, 6 bytes
On Board Device Information
Type: SATA Controller
Status: Enabled
Description: ICH10 Integrated SATA Controller
Example 7) Display Hardware Information about your system
To display the hardware information (Manufacturer, Product Name & Serial Number etc) about your system, run the following dmidecode command,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t system
# dmidecode 2.12
SMBIOS 2.5 present.
Handle 0x0002, DMI type 1, 27 bytes
System Information
Manufacturer: QCI
Product Name: QSSC-S4R
Version: ....................
Serial Number: ............
UUID: 2DD583E2-4A58-11E0-A580-00101859A783
Wake-up Type: AC Power Restored
SKU Number: Not Specified
Family: Not Specified
Handle 0x002C, DMI type 12, 5 bytes
System Configuration Options
Option 1: J5C3 2-3: Close to clear Password
Handle 0x002D, DMI type 12, 5 bytes
System Configuration Options
Option 1: J5C2 2-3: Close to clear CMOS
Handle 0x002E, DMI type 12, 5 bytes
System Configuration Options
Option 1: J6D1 2-3: Close for BIOS Recovery
Handle 0x002F, DMI type 12, 5 bytes
System Configuration Options
Option 1: J5C1 2-3: Close to Force ME Update Mode
Handle 0x0030, DMI type 12, 5 bytes
System Configuration Options
Option 1: J9C3: SATA RAID Key
Handle 0x0031, DMI type 12, 5 bytes
System Configuration Options
Option 1: J5A1 2-3: Close to Force BMC Update Mode
Handle 0x0034, DMI type 32, 20 bytes
System Boot Information
Status: No errors detected
Read More : Learn Git Command with Practical Examples on Linux – Part 1
Example 8) Display Information of about Installed Physical Memory and DIMMs
To display information about installed Physical Memory (RAM), run the below command
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t 17
# dmidecode 2.12
SMBIOS 2.5 present.
Handle 0x0043, DMI type 17, 27 bytes
Memory Device
Array Handle: 0x0035
Error Information Handle: Not Provided
Total Width: 72 bits
Data Width: 72 bits
Size: 4096 MB
Form Factor: DIMM
Set: 1
Locator: DIMM_1B
Bank Locator: MEM1 SLOT
Type: DDR3
Type Detail: Synchronous
Speed: 1067 MHz
Manufacturer: 0x0198
Serial Number: 0xA504DB27
Asset Tag: Unknown
Part Number: 9965426-047.A00LF
Handle 0x0045, DMI type 17, 27 bytes
Memory Device
Array Handle: 0x0035
Error Information Handle: Not Provided
Total Width: 72 bits
Data Width: 72 bits
Size: 4096 MB
Form Factor: DIMM
Set: 2
Locator: DIMM_1A
Bank Locator: MEM1 SLOT
Type: DDR3
Type Detail: Synchronous
Speed: 1067 MHz
Manufacturer: 0x830B
Serial Number: 0x6C443023
…………………………………………………………
In the above command output we can easily find the DIMM location, RAM Serial Number, Type and its speed.
Use below dmidecode command to find the maximum physical memory supported by your system,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t 16
# dmidecode 2.12
SMBIOS 2.5 present.
Handle 0x0035, DMI type 16, 15 bytes
Physical Memory Array
Location: Proprietary Add-on Card
Use: System Memory
Error Correction Type: Multi-bit ECC
Maximum Capacity: 256 GB
Error Information Handle: Not Provided
Number Of Devices: 8
Handle 0x0037, DMI type 16, 15 bytes
Physical Memory Array
Location: Proprietary Add-on Card
Use: System Memory
Error Correction Type: Multi-bit ECC
Maximum Capacity: 256 GB
Error Information Handle: Not Provided
Number Of Devices: 8
Handle 0x0039, DMI type 16, 15 bytes
Physical Memory Array
Location: Proprietary Add-on Card
Use: System Memory
Error Correction Type: Multi-bit ECC
Maximum Capacity: 256 GB
Error Information Handle: Not Provided
Number Of Devices: 8
……………………………………………………………
Example 9) Display Hardware information about the Processor (or CPU Sockets)
Run the below dmidecode command to display the hardware information of processor or CPU sockets
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t processor or [root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t 4 # dmidecode 2.12 SMBIOS 2.5 present. Handle 0x009B, DMI type 4, 40 bytes Processor Information Socket Designation: CPU1 Type: Central Processor Family: Xeon MP Manufacturer: Intel(R) Corporation ID: E6 06 02 00 FF FB EB BF Signature: Type 0, Family 6, Model 46, Stepping 6 Flags: FPU (Floating-point unit on-chip) VME (Virtual mode extension) DE (Debugging extension) PSE (Page size extension) TSC (Time stamp counter) MSR (Model specific registers) PAE (Physical address extension) MCE (Machine check exception) CX8 (CMPXCHG8 instruction supported) APIC (On-chip APIC hardware supported) SEP (Fast system call) MTRR (Memory type range registers) PGE (Page global enable) MCA (Machine check architecture) CMOV (Conditional move instruction supported) PAT (Page attribute table) PSE-36 (36-bit page size extension) CLFSH (CLFLUSH instruction supported) DS (Debug store) ACPI (ACPI supported) MMX (MMX technology supported) FXSR (FXSAVE and FXSTOR instructions supported) SSE (Streaming SIMD extensions) SSE2 (Streaming SIMD extensions 2) SS (Self-snoop) HTT (Multi-threading) TM (Thermal monitor supported) PBE (Pending break enabled) Version: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E7540 @ 2.00GHz Voltage: 1.2 V External Clock: 133 MHz Max Speed: 4000 MHz Current Speed: 2000 MHz Status: Populated, Enabled Upgrade: Socket LGA1567 L1 Cache Handle: 0x009D L2 Cache Handle: 0x009E L3 Cache Handle: 0x009F Serial Number: Not Specified Asset Tag: Not Specified Part Number: Not Specified Core Count: 6 Core Enabled: 6 Thread Count: 12 Characteristics: 64-bit capable …………………………………………………
Example 10) Display information about 64-bit Memory Error
To display the 64-bit Memory Error information of your system, run the beneath dmidecode command,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -t 33
Example 11) Dump dmidecode command output in Hexadecimal
In case if you don’t want to decode the dmidecode command output but you want to dump it as hexadecimal format, then use “-u” or “–dump” option in dmidecode command, example is shown below,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -u -t 4 or [root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode --dump -t 4
Note: dump option in dmidecode command becomes very handy in debugging scenarios
Example 12 ) Display dmidecode version
Use the below dmidecode command to display its version
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dmidecode -V
2.12
[root@linuxtechi ~]#
That’s all from this article, if you want to read more on dmidecode command please refer its man page. Please do share your feedback and comments.
Read More : How to Monitor Linux Systems Performance with iostat command


I am looking for a simple DMIdecode response that says either “All normal” or something is not right. If it responds with all normal then I do not need to go any further. If something is not right, then I need to dig further for answers.
I’m trying to find out similar information – where to get details about errors; Seems like folks want to keep the secrets to themselves.
Hello,
I’m getting this output:
root@NAS:~# dmidecode -H 0x14
# dmidecode 3.3
Getting SMBIOS data from sysfs.
SMBIOS 2.8 present.
51 structures occupying 2030 bytes.
Table at 0x000ECBC0.
Handle 0x0014, DMI type 8, 9 bytes
Port Connector Information
Internal Reference Designator: J3C1 – GMCH FAN
Internal Connector Type: Other
External Reference Designator: Not Specified
External Connector Type: None
Port Type: Other
So, how can I find out, how to read and control the system fan?
I didn’t find anything useful in the web.
Regards,
Tom