Ingress is one of the important concepts in Kubernetes, which allows external users to access containerized application using FQDN (fully qualified domain name). Though Ingress is not enabled and installed by default in Kubernetes cluster. We must enable to this core concept using third party ingress controllers like Nginx, Traefik, HAProxy and Istio etc.
In this tutorial we will demonstrate how to setup and use NGINX Ingress controller in Kubernetes Cluster.
As above picture, external users are accessing applications using NGINX Ingress Controller via FQDN and internal ingress controller routes the request to service and then service routes the request to backend end points or pods.
Enable NGINX Ingress Controller in Minikube
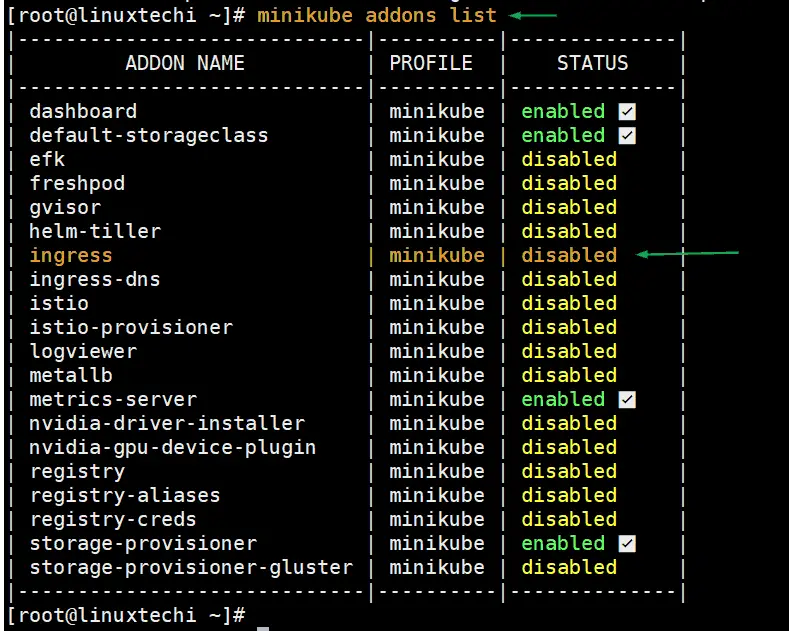
Minikube is a single node Kubernetes cluster, we can easily enable nginx ingress controller in minikube by running “minikube addons” command.
Run below command to verify the status of ingress controller,
# minikube addons list
Run following minikube command to enable ingress controller,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# minikube addons enable ingress * The 'ingress' addon is enabled [root@linuxtechi ~]#
If we re-run “minikube addons list” command, this time we must see the status of ingress is enabled.
Run following kubectl command to verify whether ingress controller’s pod is running or not.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# kubectl get pods --all-namespaces | grep -i nginx-controller kube-system ingress-nginx-controller-7bb4c67d67-gkjj5 1/1 Running 0 20m [root@linuxtechi ~]#
Above output confirms that nginx-controller has been enabled and started its pod successfully under kube-system namespace.
Setup Ingress Controller in Kubernetes Cluster (Baremetal)
Note: I am assuming Kubernetes cluster is up and running.
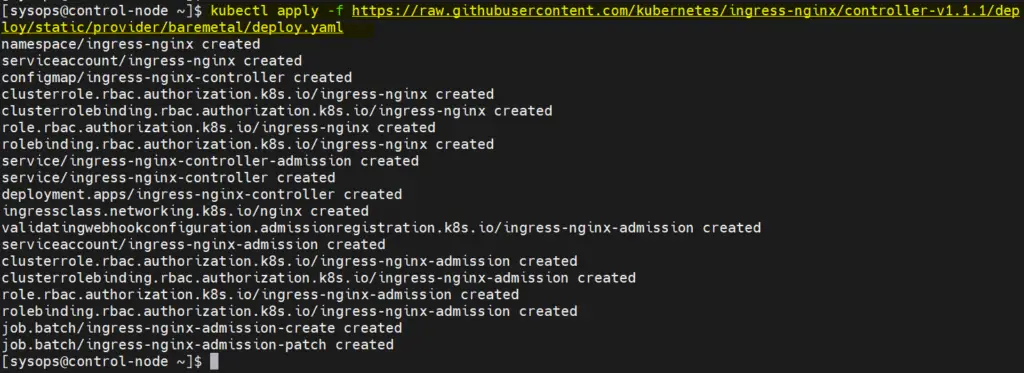
Login to master node or control plane and execute following kubectl command to install ingress.
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/controller-v1.1.1/deploy/static/provider/baremetal/deploy.yaml
Output,
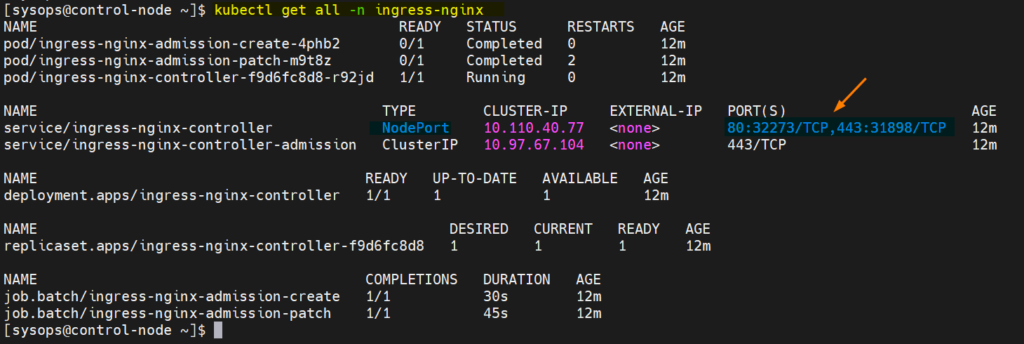
Verify the Ingress status, run beneath kubectl commands
[sysops@control-node ~]$ kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ingress-nginx-admission-create-4phb2 0/1 Completed 0 8m53s ingress-nginx-admission-patch-m9t8z 0/1 Completed 2 8m53s ingress-nginx-controller-f9d6fc8d8-r92jd 1/1 Running 0 8m53s [sysops@control-node ~]$ $ kubectl get all -n ingress-nginx
Perfect, above output confirms that Ingress controller has been install successfully.
Test Ingress Controller
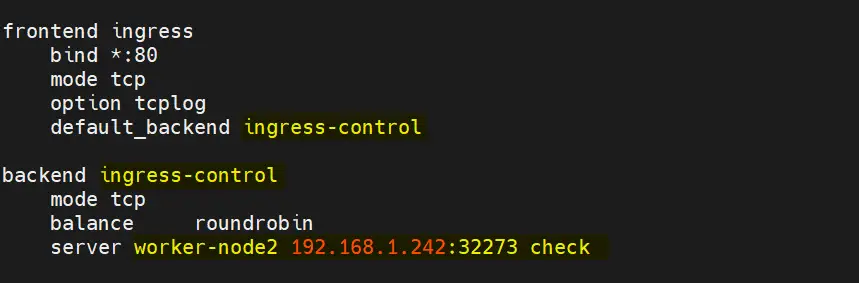
To test Ingress controller,first add the following entries in haproxy . My ingress controller pod is running on worker-node2, that’s why I have mentioned worker-node2 along with NodePort.
Save and close the file and then restart haproxy service.
Create an nginx based deployment with name ‘myapp’
$ kubectl create deployment myapp --image=nginx deployment.apps/myapp created $
Create a service by exposing the deployment with type ‘NodePort’
$ kubectl expose deployment myapp --name=myapp --type=NodePort --port=80 service/myapp exposed $
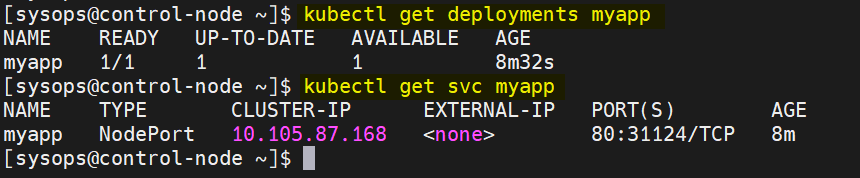
Verify the Deployment and Service status, run
$ kubectl get deployments myapp $ kubectl get svc myapp
output,
Create Ingress Resource for myapp
Create demo-ingress.yaml file with following content. When we apply this file, it will create ingress resource which will allow the application to be access from outside of kubernetes cluster via hostname. So, in this case, application hostname is ‘myapp.example.com’
$ vi demo-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-demo
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: "myapp.example.com"
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: /
backend:
service:
name: myapp
port:
number: 80
save and close the file.
Execute beneath kubectl command to create above ingress resource,
$ kubectl create -f demo-ingress.yaml ingress.networking.k8s.io/ingress-demo created $
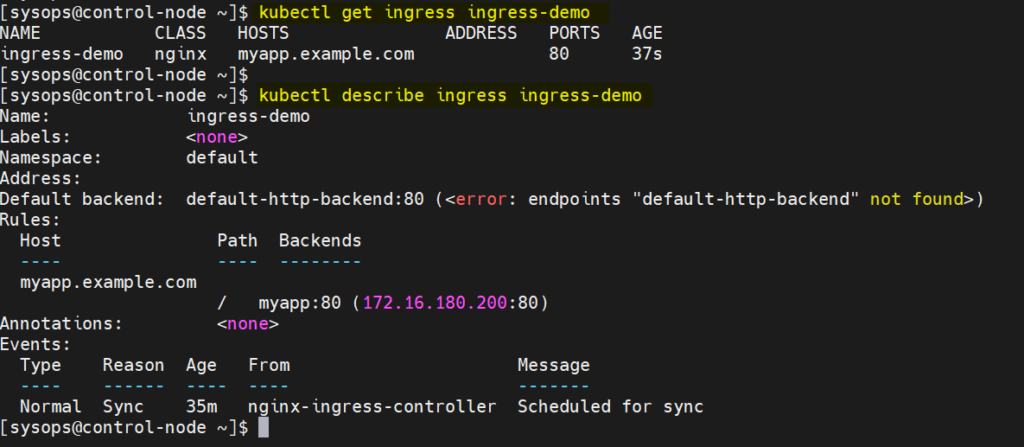
Run following to verify the status of above created ingress resource
$ kubectl get ingress ingress-demo $kubectl describe ingress ingress-demo
Perfect, above output confirms that ingress resources have been created successfully.
Before accessing these urls from outside of the cluster please make sure to add the following entry in hosts file of your system from where you intended to access these.
192.168.1.240 myapp.example.com
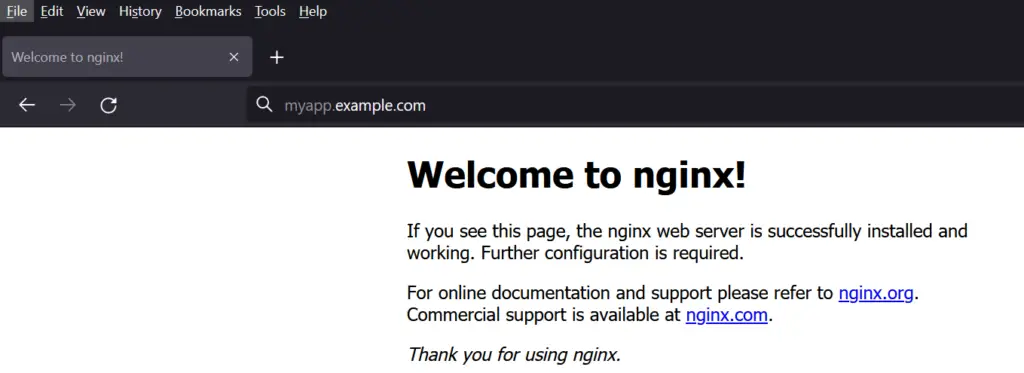
Now try to access URL from web browser, type
http://myapp.example.com
Great, above confirms that we have successfully deployed and setup nginx ingress controller in Kubernetes. Please do share your valuable feedback and comments.
Hello, I have tried the procedures above, but finally failed.
When I enter the command curl httpd.example.com:80 / nginx.example.com:80 in k8s master, it returns curl: (7) Failed to connect to httpd.example.com port 80: Connection refused.
Do you have any idea about the error?
Hi David,
If the above procedure does not work for you then I would suggest download ingress deploy yaml file and then edit it and add following in deployment section
spec:
hostNetwork: true
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
containers:
Save and exit the file and try to redeploy the ingress with the updated yaml file.
Hi Pradeep,
I have downloaded the ingress deploy yaml file and add the following
spec:
hostNetwork: true
but it seems that it failed as well.
Finally it seems it is ok after I added the following in httpd-deployment.yaml and nginx-deployment.yaml.
externalIPs:
– “192.168.30.5”
I believe above won’t work directly unless you assign an external ip to ingress controller service ( external ip can be assigned automatically using MetalLB )
Please refer below,
‘https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/deploy/’
‘https://metallb.universe.tf/’
Hi,
I am performing this on EC2 instance and facing the same connection refused error, Please suggest me anything