In this post, we will show you how to create and extend xfs file system based on LVM.
XFS is a file system which is designed for high performance ,scalability and capacity point of view. It is generally used where large amount data to be stored / used on the File system. Some of the awesome freeze features of xfs are xfs_freeze, snapshot, xfs_unfreeze. One of the limitation of XFS is that we can not shrink or reduce this file system.
XFS is the default file system in the modern Linux distributions like RHEL 8/9, Fedora, Rocky Linux, AlmaLinux and Ubuntu. We are assuming that a new disk (/dev/sdb) is already assigned to Linux system and we are going to perform below steps on that disk.
Without any further delay, let’s deep dive into the steps.
Step 1) Install LVM2 Package
To create LVM partitions on Linux, make sure lvm2 package is installed. In case, it is not installed then run following command,
$ sudo apt install -y lvm2 //Ubuntu & Debian System # yum install lvm2 -y // RHEL 7 & CentOS 7 or # dnf install lvm2 -y // RHEL 9/8, Rocky Linux & AlmaLinux
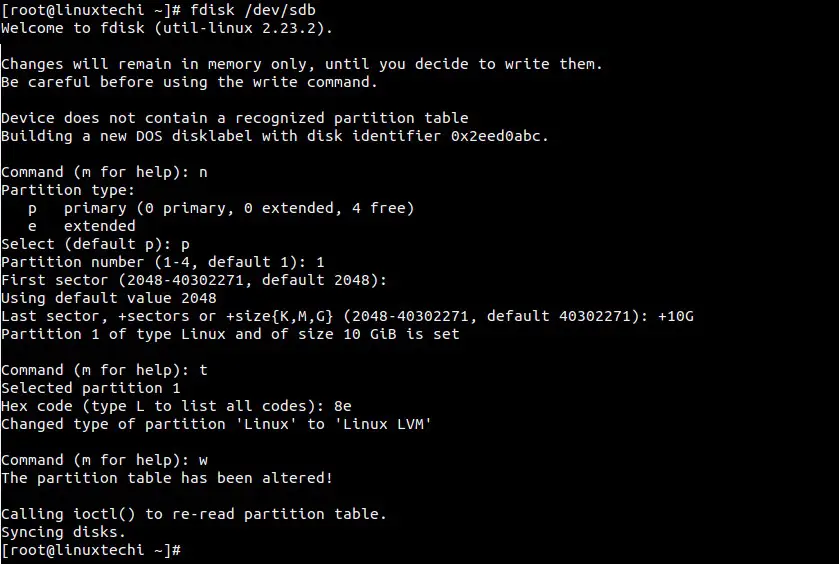
Step 2) Create Partition using fdisk
In the below example, we have created 10GB partition on /dev/sdb using fdisk command and set “8e” as toggle id.
Step 3) Create LVM Components (pvcreate, vgcreate and lvcreate)
[root@linuxtechi ~]# pvcreate /dev/sdb1 Physical volume "/dev/sdb1" successfully created [root@linuxtechi ~]# [root@linuxtechi ~]# vgcreate vg_xfs /dev/sdb1 Volume group "vg_xfs" successfully created [root@linuxtechi ~]# [root@linuxtechi ~]# lvcreate -L +6G -n xfs_db vg_xfs Logical volume "xfs_db" created [root@linuxtechi ~]#
Step 4) Format LVM Partition as XFS File System
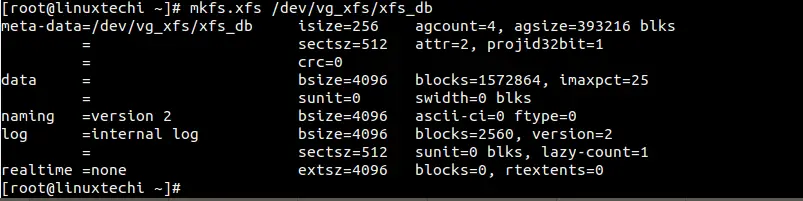
Run the following mkfs.xfs command to format lvm,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/vg_xfs/xfs_db
Step 5) Mount the xfs file system
Create a directory named as xfs_test under /root and mount it using mount command. Run following set of commands,
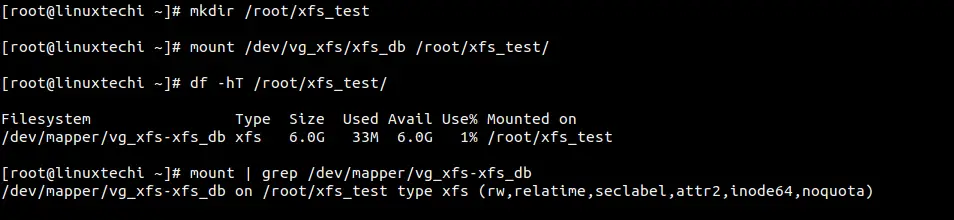
For the permanent mounting , add the entry in /etc/fstab file.
Step 6) Extend the size of xfs file system
Check the whether free space is available in Volume group (vg_xfs) or not using below command :
[root@linuxtechi ~]# vgs vg_xfs VG #PV #LV #SN Attr VSize VFree vg_xfs 1 1 0 wz--n- 10.00g 4.00g [root@linuxtechi ~]#
So, we will extend the file system by 3GB using lvextend command with “-r” option
[root@linuxtechi ~]# lvextend -L +3G /dev/vg_xfs/xfs_db -r
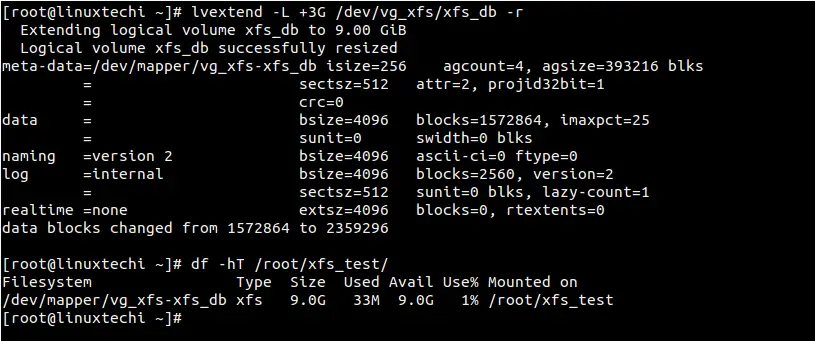
As we can see above that the size of “/dev/vg_xfs/xfs_db” has been extended from 6 GB to 9GB
Note : If xfs is not based on LVM , the use the xfs_growsfs command as shown below :
[root@linuxtechi ~]# xfs_growfs <Mount_Point> -D <Size>
The “-D size” option extend the file system to the specified size (expressed in file system blocks). Without the -D size option, xfs_growfs will extend the file system to the maximum size supported by the device.
Read Also : How to Setup Disk Quota on XFS File System in Linux Servers
Hi,
Can you explain the full steps for reduce lvm in RHEL 7.
One of the limitation of XFS is that we can not shrink or reduce this file system. On XFS file system
hello, could we format the XFS filesystem with a block size 4096 and sector size 512 ? how could we do it ? and then add the entry in /etc/fstab file. could you pls show us the steps.
what does -r option in lvmextend using for?
The -r option automatically grows the file system.
no need to run resize2fs after the lvextend
hi,
i have one query when we extend xfs file we use xfs_growfs command , may i know when we reduce xfs file-system which command use, like in ext3 we use resize2fs for both reduce /extend.
File system reduction is not possible in XFS.
what do you mean by xfs not based on lvm?? is there any chance that we can grow a non lvm partition??
Hi Nanada,
Non lvm XFS file system can be extended using ‘xfs_growfs’ command
great job !
works like a charm
If I want to use the whole disk, do I need to partition it before pvcreate? doesn’t pvcreate do the alignment for you?
No need to create partition on disk if you are planning to create physical volume on the whole disk.
example : # pvcreate /dev/sdc
Thank you for this tutorial! Only one missing thing: I needed to install LVM2 package to use certain commands. Might be helpful to add such note. Thanks again!