SFTP stands for Secure File Transfer Protocol / SSH File Transfer Protocol, it is one of the most common method which is used to transfer files securely over ssh from our local system to remote server and vice-versa. The main advantage of sftp is that we don’t need to install any additional package except ‘openssh-server’, in most of the Linux distributions ‘openssh-server’ package is the part of default installation. Other benefit of sftp is that we can allow user to use sftp only not ssh.
Recently Debian 10, Code name ‘Buster’ has been released, in this article we will demonstrate how to configure sftp with Chroot ‘Jail’ like environment in Debian 10 System. Here Chroot Jail like environment means that user’s cannot go beyond from their respective home directories or users cannot change directories from their home directories. Following are the lab details:
- OS = Debian 10
- IP Address = 192.168.56.151
Let’s jump into SFTP Configuration Steps,
Step:1) Create a Group for sftp using groupadd command
Open the terminal, create a group with a name “sftp_users” using below groupadd command,
root@linuxtechi:~# groupadd sftp_users
Step:2) Add Users to Group ‘sftp_users’ and set permissions
In case you want to create new user and want to add that user to ‘sftp_users’ group, then run the following command,
Syntax: # useradd -m -G sftp_users <user_name>
Let’s suppose user name is ’Jonathan’
root@linuxtechi:~# useradd -m -G sftp_users jonathan
set the password using following chpasswd command,
root@linuxtechi:~# echo "jonathan:<enter_password>" | chpasswd
In case you want to add existing users to ‘sftp_users’ group then run beneath usermod command, let’s suppose already existing user name is ‘chris’
root@linuxtechi:~# usermod -G sftp_users chris
Now set the required permissions on Users,
root@linuxtechi:~# chown root /home/jonathan /home/chris/
Create an upload folder in both the user’s home directory and set the correct ownership,
root@linuxtechi:~# mkdir /home/jonathan/upload root@linuxtechi:~# mkdir /home/chris/upload root@linuxtechi:~# chown jonathan /home/jonathan/upload root@linuxtechi:~# chown chris /home/chris/upload
Note: User like Jonathan and Chris can upload files and directories to upload folder from their local systems.
Step:3) Edit sftp configuration file (/etc/ssh/sshd_config)
As we have already stated that sftp operations are done over the ssh, so it’s configuration file is “/etc/ssh/sshd_config“, Before making any changes I would suggest first take the backup and then edit this file and add the following content,
root@linuxtechi:~# cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config-org root@linuxtechi:~# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config ……… #Subsystem sftp /usr/lib/openssh/sftp-server Subsystem sftp internal-sftp Match Group sftp_users X11Forwarding no AllowTcpForwarding no ChrootDirectory %h ForceCommand internal-sftp …………
Save & exit the file.
To make above changes into the affect, restart ssh service using following systemctl command
root@linuxtechi:~# systemctl restart sshd
In above ‘sshd_config’ file we have commented out the line which starts with “Subsystem” and added new entry “Subsystem sftp internal-sftp” and new lines like,
“Match Group sftp_users” –> It means if a user is a part of ‘sftp_users’ group then apply rules which are mentioned below to this entry.
“ChrootDierctory %h” –> It means users can only change directories within their respective home directories, they cannot go beyond their home directories, or in other words we can say users are not permitted to change directories, they will get jai like environment within their directories and can’t access any other user’s and system’s directories.
“ForceCommand internal-sftp” –> It means users are limited to sftp command only.
Step:4) Test and Verify sftp
Login to any other Linux system which is on the same network of your sftp server and then try to ssh sftp server via the users that we have mapped in ‘sftp_users’ group.
[root@web-server ~]# ssh [email protected] [email protected]'s password: Write failed: Broken pipe [root@web-server ~]# ssh [email protected] [email protected]'s password: Write failed: Broken pipe [root@web-server ~]#
Above confirms that users are not allowed to SSH , now try sftp using following commands,
[root@web-server ~]# sftp [email protected] [email protected]'s password: Connected to 192.168.56.151. sftp> ls -l drwxr-xr-x 2 root 1001 4096 Sep 14 07:52 debian10-pkgs -rw-r--r-- 1 root 1001 155 Sep 14 07:52 devops-actions.txt drwxr-xr-x 2 1001 1002 4096 Sep 14 08:29 upload
Let’s try to download a file using sftp ‘get‘ command
sftp> get devops-actions.txt Fetching /devops-actions.txt to devops-actions.txt /devops-actions.txt 100% 155 0.2KB/s 00:00 sftp> sftp> cd /etc Couldn't stat remote file: No such file or directory sftp> cd /root Couldn't stat remote file: No such file or directory sftp>
Above output confirms that we are able to download file from our sftp server to local machine and apart from this we have also tested that users cannot change directories.
Let’s try to upload a file under “upload” folder,
sftp> cd upload/ sftp> put metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb Uploading metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb to /upload/metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb 100% 38MB 38.4MB/s 00:01 sftp> ls -l -rw-r--r-- 1 1001 1002 40275654 Sep 14 09:18 metricbeat-7.3.1-amd64.deb sftp>
This confirms that we have successfully uploaded a file from our local system to sftp server.
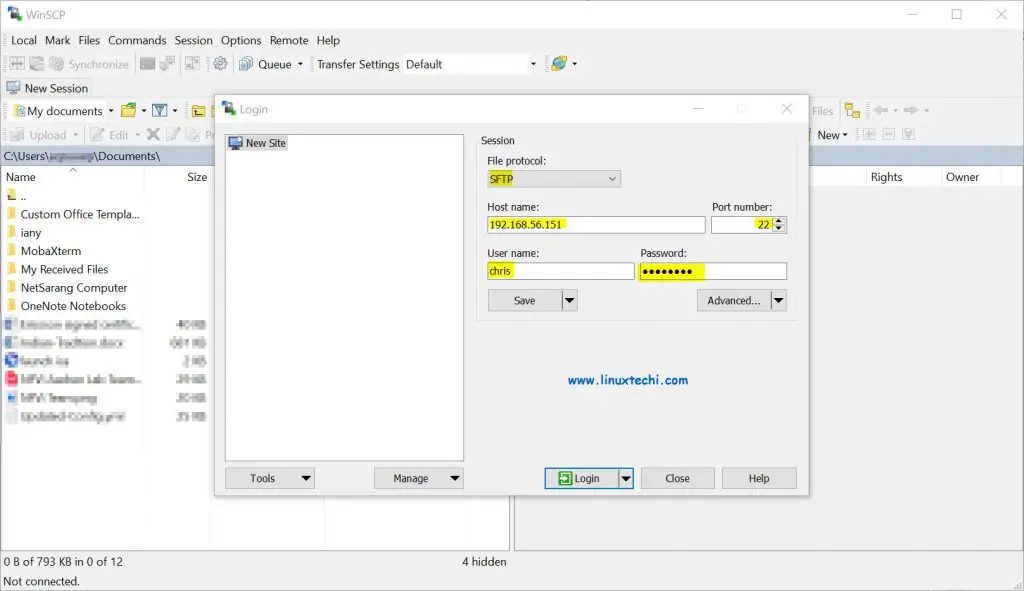
Now test the SFTP server with winscp tool, enter the sftp server ip address along user’s credentials,
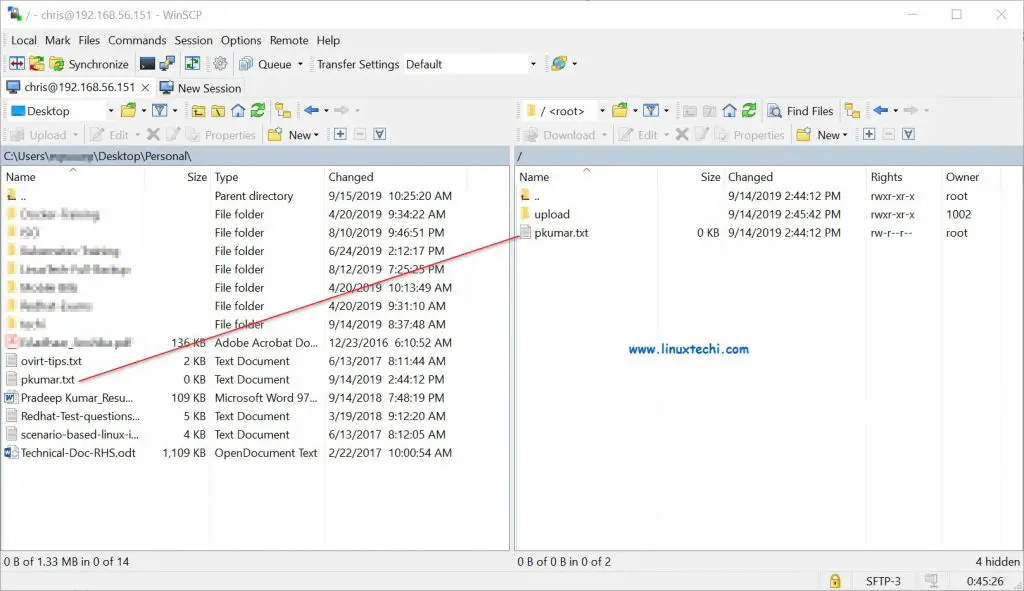
Click on Login and then try to download and upload files
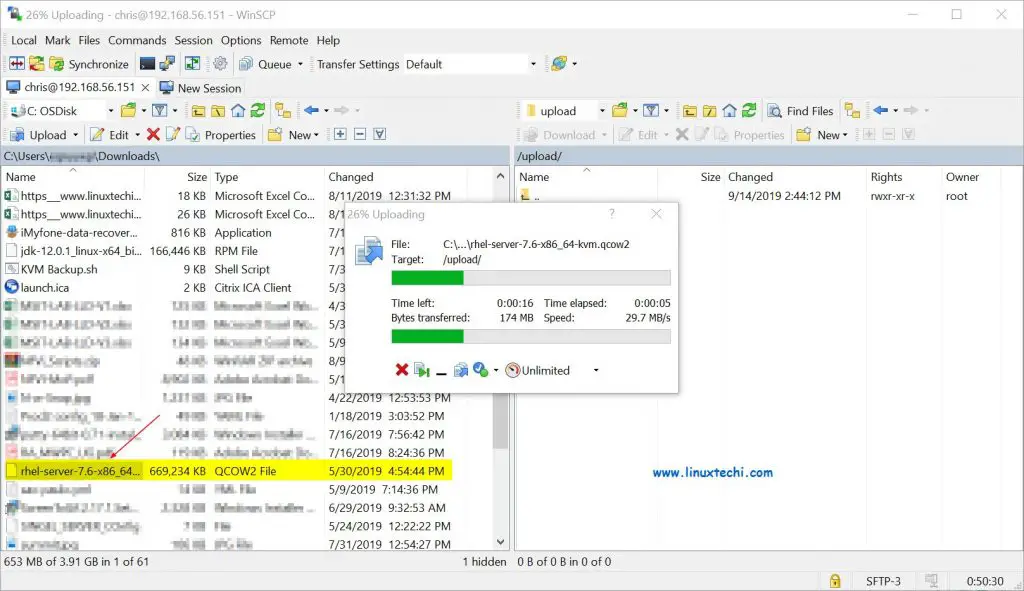
Now try to upload files in upload folder,
Above window confirms that uploading is also working fine, that’s all from this article. If these steps help you to configure SFTP server with chroot environment in Debian 10 then please do share your feedback and comments.

Please describe internal-sftp,
%h,
I unable to ls -l and pad, cd, get and put command. permission denied,
Please describe.
%h means users will directly land into its home directory when they do sftp command.
internal-sftp is a configuration keyword that tells sshd to use SFTP server code built-into sshd.
You need to set the required permissions on User’s home directory
You can also try SFTPGo
‘https://github.com/drakkan/sftpgo’
it has chroot support builtin, virtual quota, atomic uploads, bandwidth throttling and many other features.
It can execute configurable custom commands and/or send HTTP notifications on upload, download, delete or rename.
It is written in Go, so no runtime dependencies, and it works on Windows too
I followed this guide and it worked for me, at least until I rebooted the host. Now, every time I test the connection using WinSCP or Filezilla, its trying to open / folder instead of redirecting to the subfolder under the homefolder for the user. Can’t figure it out, any ideas?
Possible to enable an RSA fingerprint or RSA Key? Or is username / password the only authentication method?
^ This. I added SSH key in and server refuses everytime and requires password
Make the public key directory – mkdir /home/$User/.ssh
Make the key file to hold the key touch /home/$User/.ssh/authorized_keys
Give the user ownership of their key folder – chown $User:$User /home/$User/.ssh && chown $User:$User /home/$User/.ssh/authorized_keys
Modify permissions on ssh folder – chmod 0700 /home/$User/.ssh
Possibly modify the key file permissions – chmod 640 /home/$User/.ssh/authorized_keys <— Not 100% if this needs to be done try without it first and if it wont work add it in
Add the public key – /home/$User/.ssh/authorized_keys
Restart ssh – systemctl restart sshd